Have you ever wondered what gives cannabis its distinctive aroma and flavor? These delightful compounds are called terpenes, or aromatic compounds, and can be found in all plants. Not only do they contribute to the unique scents we love, but they also enhance the effects of cannabis by working together with cannabinoids. Learn more about the amazing benefits of terpenes and discover their crucial role in customizing your cannabis experience.

Table of Contents
Article Features
- The five most common terpenes in cannabis
- Potential health benefits associated with terpenes
- Want to skip the hard work? Shop with me and have premium, high-quality cannabis products delivered directly to your door! Now shipping across the US.

Why You Will Love This Guide
The beautiful, yet distinctive, the aroma of cannabis is just one part of what makes this plant so incredible.
Whether it be the fruity smell of Tangerine Dream or the strong lemon aroma from a Sour Haze, each cannabis strain has its own specific aroma and effect.
But what makes the unique aroma of each strain?
The answer is terpenes.
Found in all plants, these compounds are present in cannabis, too, and have their own potential health benefits.
In this guide, we will explore terpenes further, including the ones that are most commonly found in cannabis, and how you can use them to customize your experience.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are aromatic oils found in the flowers, bark, seeds, leaves, stems, and roots of all herbs, spices, fruits, and vegetables.
You’re probably already familiar with different terpenes associated with common smells like citrus, berry, mint, and pine.
Terpenes are responsible for the smell of cannabis, a freshly picked peach, and the scent of a bouquet of fresh flowers.
Terpenes are contained within the trichomes of the cannabis plant.
Along with cannabinoids, terpenes are responsible for exerting various physiological effects on the human body1.
To date, there have been over 10,000 different types of terpenes identified2.
Between 10-30 different types of terpenes can be present in any given cannabis plant, and the concentrations and ratios will vary from strain to strain.
Terpenes have medicinal properties, including powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects1, and also present their own anti-anxiety, anti-depressant, pain relief, and sedative effects3.
Compared to traditional dried cannabis, raw cannabis will retain most of its terpenes, lending to the potential health benefits of consuming raw cannabis.
The effects of different terpenes range from euphoric to energized, creative and focused, and of course, relaxed.
Although some differences may be subtle, terpenes can add great depth to the cannabis experience, its unique medicinal properties, and its psychoactive effects.
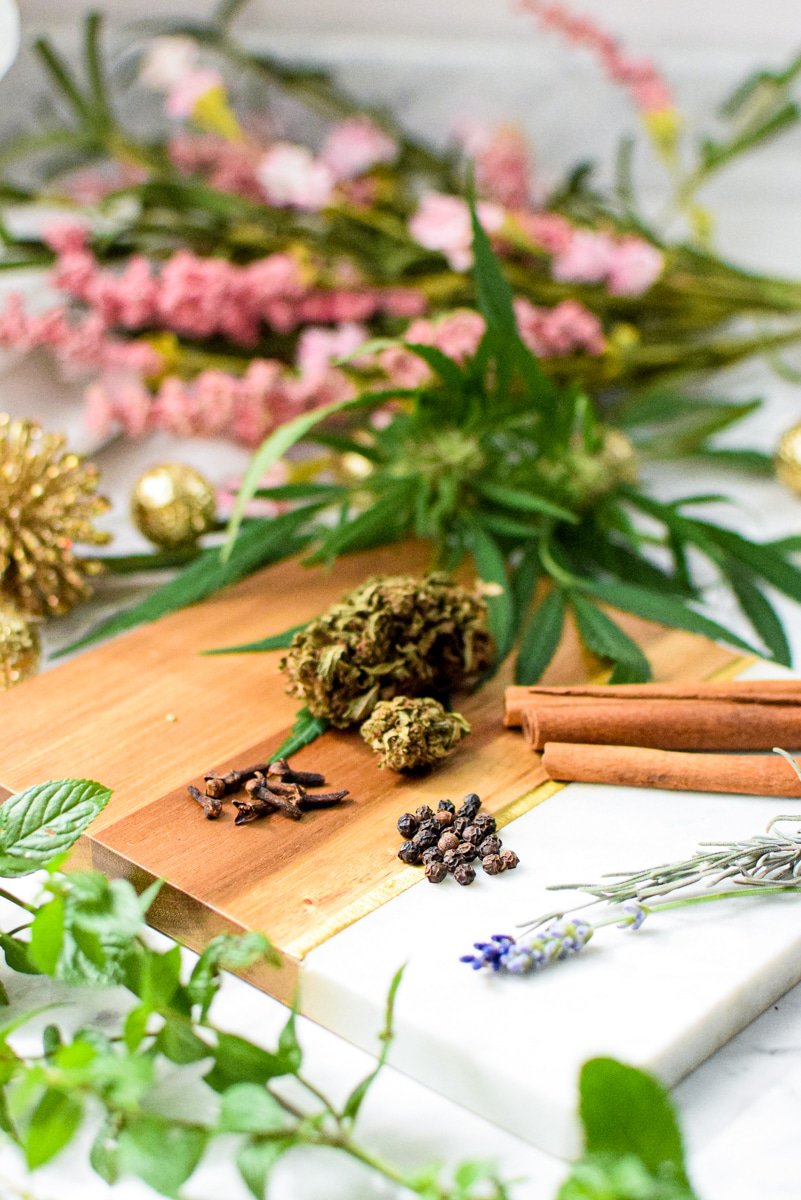

The Benefits of Terpenes
Beyond taste and smell, there is an incredible amount of science to support the health benefits of terpenes.
The unique combination of cannabinoids and terpenes is responsible for the differences in the effects of various strains.
Like cannabinoids, terpenes contribute to the beneficial full-spectrum effect of cannabis, also known as the entourage effect.
Terpenes work alongside other cannabinoids and affect the body’s own endocannabinoid system.
In turn, we can learn how to use them to improve our own health and wellness.
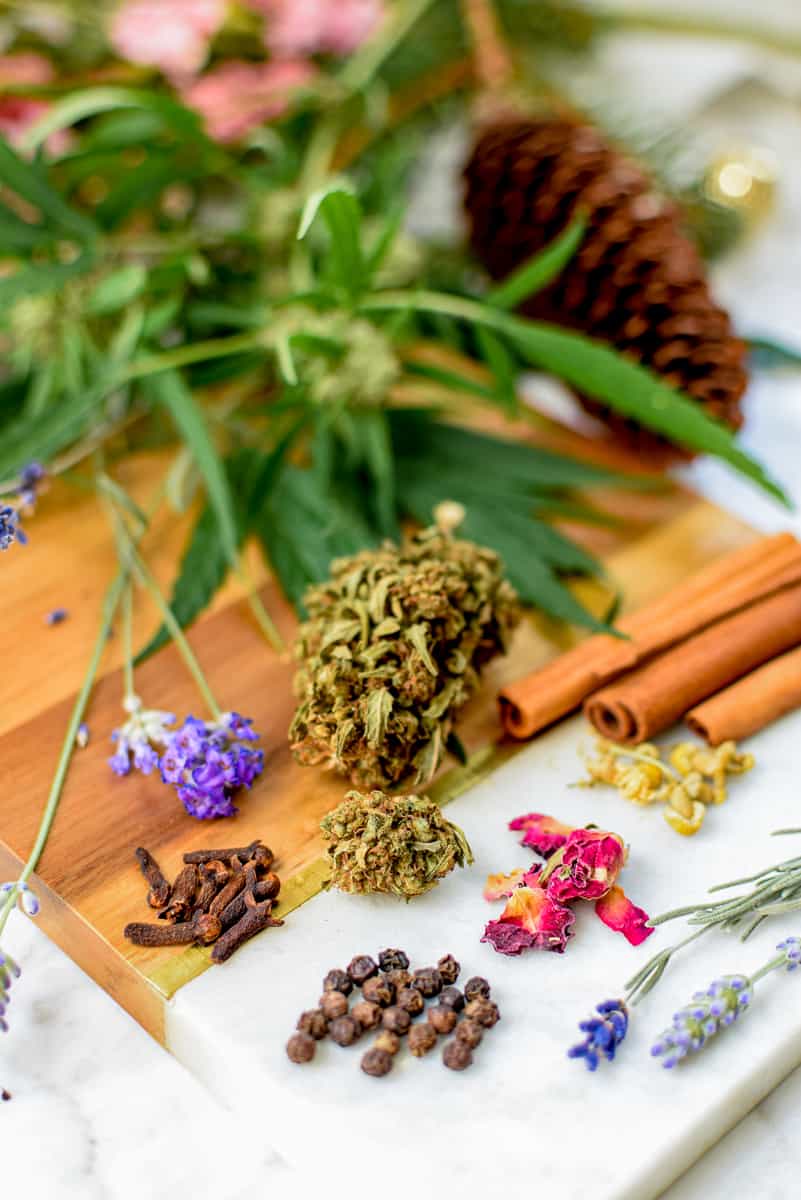

Terpenes Found in Cannabis
The cannabis plant contains a variety of terpenes with the actual composition varying from strain to strain.
These compounds interact with multiple physiological systems in the body, exerting a variety of effects.
The most common terpenes found in cannabis are:
- Myrcene
- Beta-caryophyllene
- Limonene
- Linalool
- Pinene
- Terpinolene
- Humulene
- Ocimene
- Nerolidol
Myrcene
Myrcene is the most abundant monoterpene found in cannabis4.
Myrcene produces pain-relieving effects as a result of potential activity at the alpha-2 adrenoreceptors5.
Along with being a pain reliever, myrcene also has anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and sedative effects.
Myrcene has been historically used as a muscle relaxant to soothe muscle spasms and may even induce liver detoxification enzymes.
While most abundant in cannabis, myrcene is also found in mangoes, hops, lemongrass, basil, and thyme.
Beta-Caryophyllene
Beta-caryophyllene is the most abundant sesquiterpene found in cannabis.
This terpene acts as an agonist of CB2 receptors within the endocannabinoid system.
According to the National Academy of Sciences, B-caryophyllene has neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-fungal, anti-malarial, and anti-cancer properties6.
Beta-caryophyllene is also found in black pepper, cardamom, cloves, oregano, rosemary, and carrot seed.
Limonene
Limonene is a highly bioavailable monoterpene commonly found in citrus oils.
According to Bioscience Reports, limonene is an immunostimulant that has been studied for its anti-cancer, anti-microbial, anti-depressant, anti-anxiety, anti-spasmodic, and powerful antioxidant properties7.
It is speculated that the antispasmodic properties found in citrus oil may potentially strengthen the treatment against painful intestinal conditions.
It has also been reported in traditional herbal medicine that limonene is an antidote against cannabis intoxication.
Limonene is also found in lemons, oranges, grapefruits, pineapple, apricots and more.
Linalool
Linalool is a terpene that produces the familiar scent associated with lavender and other plants.
According to a review published in Colloids and Biointerfaces, this terpene has been studied for its anti-depressant, pain relief, anti-convulsant, anti-anxiety, anti-tumor, and anti-fungal properties8.
Linalool affects the nervous system, can act as a local anesthetic, and is a primary example of essential oil being used to relieve anxiety and help sleep.
Using other botanicals, like lavender, in conjunction with cannabis to achieve a specific effect is referred to as herbal synergy.
The calming and sedative effects of lavender may be beneficial in aiding CBD to reduce the intoxicating effects of THC.
A lavender essential oil may also affect CB2 receptors in the skin.
Linalool is also found in lavender, holy basil, cilantro, and more.
Pinene
Alpha-pinene and beta-pinene are monoterpenes commonly found in pine needles.
Pinene works to relieve pain and acts as an anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, antibacterial, bronchodilator and is neuroprotective9.
The analgesic properties of both pine and cannabis can be combined for both intestinal pain and arthritis pains.
Pinene is commonly found in conifers like pine and hemlock trees.
Frequently Asked Questions
Terpenes derived from plants other than cannabis are recognized by the FDA as a food additive and are classified as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) (3).
No, these volatile organic compounds, or aromatic essential oils, determine the smell and taste are present in all types of plants.










Hi Emily,
Do you think that FECO/RSO’s process destroys the terpenes, or they may be intact even with the heating and everything? (Since in your post you mentioned that they are more present in raw cannabis.)
For FECO I’ve been choosing cannabis plants that have plenty of limonene, caryophyllene and linalool for my husband to fight against cancer and seizures.
Thank you for this amazing post!
Hi Viviam. FECO stands for “Full-Extract Cannabis Oil” and by full-extract it means that all of the important plant compounds, from cannabinoids to terpenes and other plant materials, are present in the extract. The alcohol pulls everything from the plant. If you’re heating your tincture to evaporate down to FECO, you may be killing off some terpenes though, along with some cannabinoids. I hope this helps!
Where can you find the best terpenes for a certain medical condition.
Hello Andrea, the terpenes that will work best for you and your specific condition will be unique to *you*. Its best to experiment to see what works with your body!